Definition of injection molding or injection of plastic material
Injection of plastic material or injection molding is a parts manufacturing process ranging from small series to large series of over thousands of parts.
The details of plastic injection molding
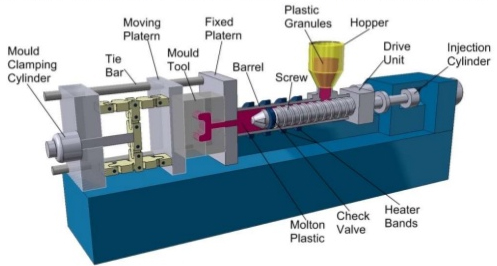
The plastic injection process generally follows this pattern.
The first step is the design and manufacturing of one mold. This step will be entrusted to a mold maker such as Unimold. The mold consists of two parts, one fixed and one movable. The choice of the mold’s raw material as well as the quality of its components have a strong influence on its productivity and its length of service life.
The second step requires placing the mold in an injection press. The two side of the mold will be strongly pressed against each other and then separated to allow ejection of the part. The mold may also include one or more movements used to form some undercut shape. Inserts can also be implemented. These will be included in the final part.
The third step is the injection of the thermoplastic material. The material in the form of pellets is poured into a plasticising screw that is heated. Its rotation allows injecting the melted material into the mold. It is important to ensure that the filling of the cavity is complete before the material solidifies. This is why the injection screw continues to exert pressure on the material after the injection; this is referred to as the maintenance phase.
The part is then cooled through cooling circuits inside the mold. It is then ejected, and the next cycle can begin.
The applications of plastic injection



Plastic injection parts are used in many areas: the automotive industry, electronics, aerospace, and in the medical sector. But also in everyday life: children’s toys, garden furniture, computers, electronic product housings, saucepan handles and so on.
The advantages of plastic injection molding
The main advantage is to be able to produce within a single operation final parts having more or less complex finishes and forms.
Injection molding enables the production of high quality parts. For this reason, extremely demanding industries such as automotive, medical, and aerospace resort to this technique.
The limits of plastic injection molding
The initial limitation is the cost of designing the mold. For a steel mold, the profitability of the project is possible only when producing large quantities of at least 100 parts.
The second point is the service life of the mold, which varies according to the chosen raw material. Aluminium will be initially less expensive than steel but has a lower service life expectancy. Another limitation is the mold’s manufacturing time, which is much longer than 3D printing, for example.
